What is uveitis? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Uveitis requires immediate medical attention, and patients can go in for treatment. Medical experts do the needful and try to protect vision, which can get affected.
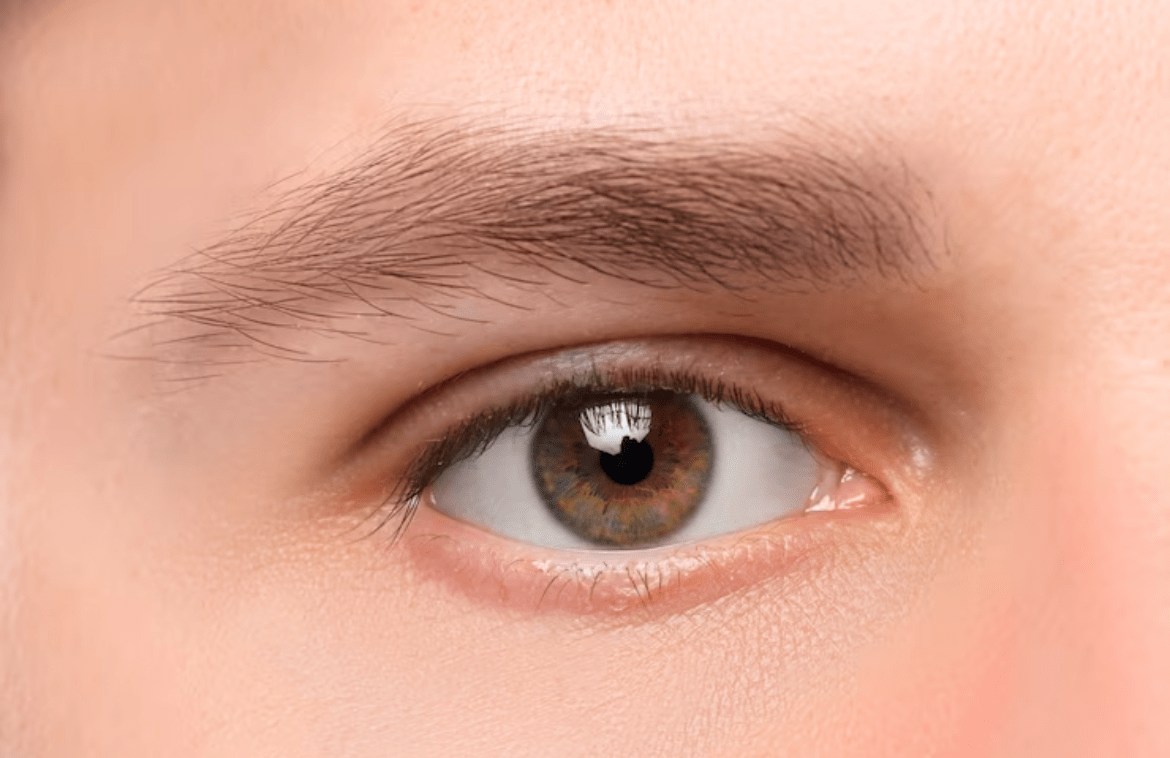
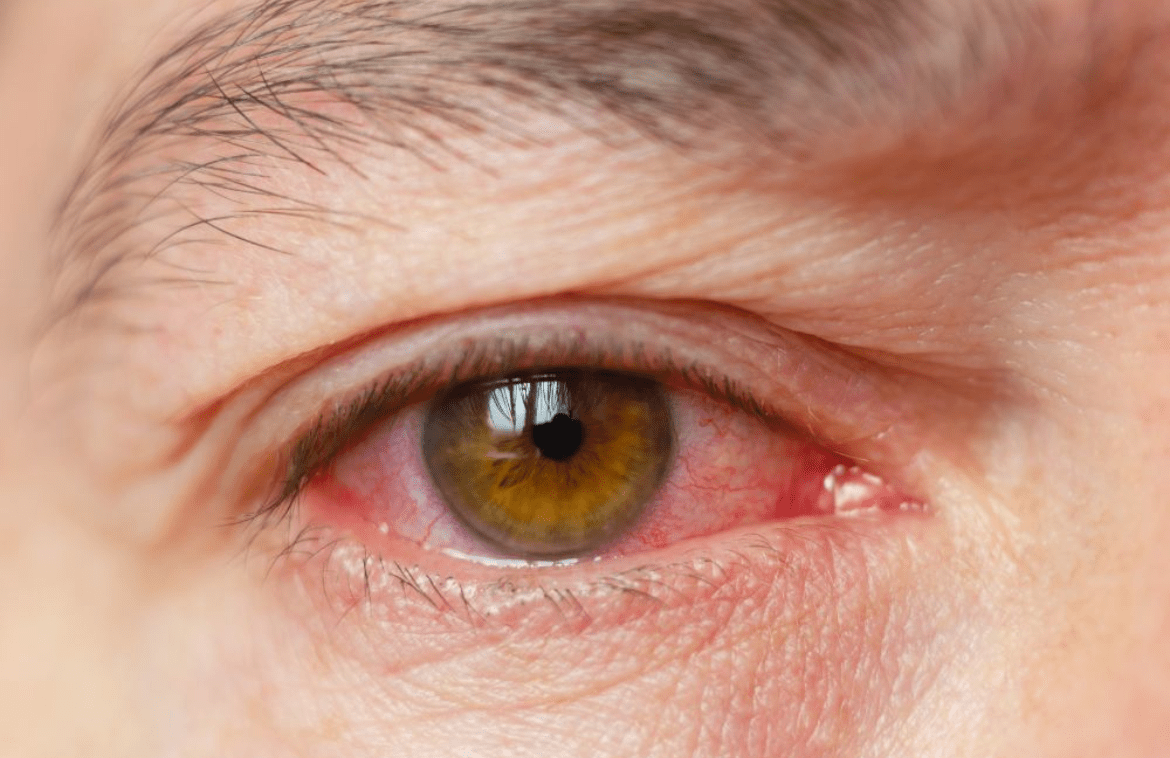
Uveitis happens to be a form of eye inflammation that affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea).
Uveitis (u-vee-I-tis) warning signs often come on suddenly and get worse rather quickly. They do include eye redness, pain, and blurred vision. The condition can in fact affect one or both eyes, and it can affect people of all ages, even children.
Possible causes of uveitis are infection, injury, or even an autoimmune or inflammatory disease. Many times, a cause is difficult to identify.
Uveitis can indeed be serious, leading to permanent vision loss. Early diagnosis as well as treatment are important to prevent complications and preserve one’s vision.
Uveitis is a form of eye inflammation that does affect the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea). The condition can affect one or both eyes, and it can also affect people of all ages, even children. Symptoms of uveitis tend to differ depending on the type.
Common symptoms include
- Swelling of the middle layer (uvea).
- Redness in the eye.
- Eye pain.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Floaters in the field of vision.
- A decrease in one’s vision.
- Blurred vision.
- Alteration in the color of the iris.
- A small pupil.
Symptoms may indeed occur suddenly and get worse quickly, though in some cases, they do develop gradually. They may affect one or both eyes. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms, and signs of uveitis are observed on a routine eye exam.
The uvea is the middle layer of tissue in the wall of the eye and consists of the iris, the ciliary body, and the choroid. When a person looks at one’s eye in the mirror, he or she will see the white part of the eye (sclera) and the colored part of the eye (iris).
The iris is, in fact, located inside the front of the eye. The ciliary body is a structure behind the iris. The choroid is a layer of blood vessels between the retina as well as the sclera. The retina lines the inside of the back of the person’s eye, like wallpaper. The inside of the back of the eye is filled with a gel-like liquid known as vitreous.
Causes of uveitis include:
- An eye injury.
- Trauma or perhaps eye surgery.
- Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
- Inflammatory disorders such as Kawasaki disease and Crohn’s disease.
- An eye infection.
- There are a few cancers that can affect the eye, like leukemia, lymphoma, and melanoma (all rare).
A few of the many disorders that can cause uveitis include:
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Herpes simplex
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Leptospirosis
- Herpes zoster
- Lupus
- Lyme disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Syphilis
- Toxocariasis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis
Also, smoking is another risk factor for uveitis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis does entail an examination of the eye and the underlying cause. Further tests are often decided based on the suspected causes.
Treatment
Treatment procedures do indeed vary greatly from case to case, depending on the underlying cause as well as specific symptoms. It can be treated with medication, usually glucocorticoids. If the person or someone the person knows is exhibiting symptoms of uveitis, seeking medical attention immediately is a good idea.

What is uveitis? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
If the eye doctor decides the person has uveitis, he or she will likely prescribe a steroid to reduce the inflammation in the eye.
Whether the steroid is administered as an eye drop, pill, or injection depends on the type of uveitis a person has. Because iritis does affect the front of the eye, it is usually treated with the help of eye drops.
Posterior uveitis requires tablets or injections. Steroids and other immune suppressants can produce several serious side effects, like kidney damage, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, and glaucoma.
Conclusion
Contacting the doctor if you observe warning signs of uveitis does help.







There are no comments